Shipping agricultural machinery to Egypt can be a complex task. This process requires careful planning, navigating international regulations and restrictions, and knowing the nuances of farm equipment shipping.
Atlantic Project Cargo is a team of dedicated professionals that can help you import farm equipment to Egypt. Our company specializes in transporting oversized cargo across borders and continents, and we have 20+ years of experience.
What Are the International Transportation Modes of Farm Equipment to Egypt?
Egypt’s rich agricultural history owes much to its efficient logistics network. Importing farm equipment can use multi-modal transportation, and each method has its advantages and considerations. Let’s have a look at available methods of shipping.
Ocean Freight
The dominant mode, especially for bulky machinery like tractors and harvesters. Containerized shipping from Europe, North America, and Asia offers cost-effectiveness for large volumes. Other ocean freight methods include Ro-Ro vessels and breakbulk ships. Main ports like Alexandria and Damietta serve as entry points, with inland networks like the Nile River and highways facilitating further movement.
Air Cargo
Fastest, but most expensive option. Air freight can be chosen for time-sensitive equipment or spare parts. The weight limit depends on the air freight company and varies from 5.000 kg to 15.000 kg (11.000 lbs. and 35.000 lbs). Kairo International Airport is a key hub for such cargo.
Land Transportation
Used for shorter distances or within Egypt itself. Trucks equipped for oversized cargo handle specific machinery movements between ports, warehouses, and farms. This mode offers flexibility and point-to-point delivery but comes with limitations based on infrastructure and distance.
Specialized Carriers
Some equipment, like irrigation systems or delicate sensors, require temperature-controlled or specially-equipped vehicles or containers. Usage of specialized vehicles or containers is crucial for safe and optimal transportation.
How to Choose the Right Transportation Method?
The choice depends on several factors:
- Type and size of equipment
Bulky machinery can be transported by sea, while fragile equipment like agribots requires air cargo - Urgency
Fastest option – air, cost-effective – ocean - Distance
For short cross-border distances, truck transportation can be an option - Budget
Costs vary significantly between modes, impacting the final decision
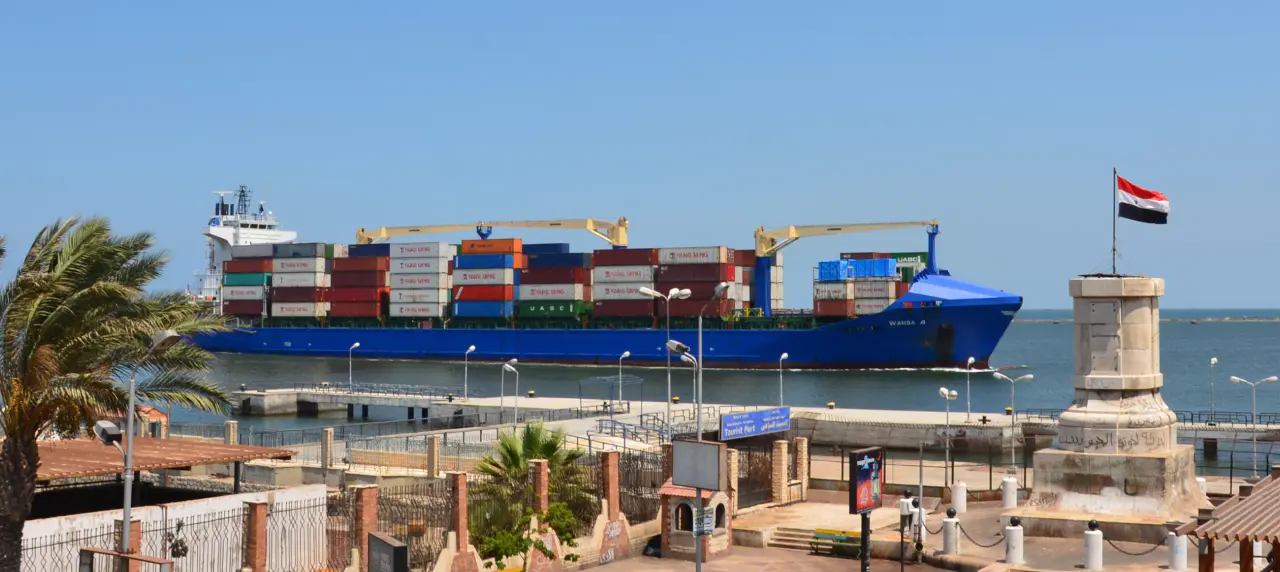
What Are the Main Shipping Ports in Egypt?
Today, Egypt’s network of ports plays a vital role in the nation’s economy, serving as gateways for international trade. The main ports include:
- Alexandria and El Dekheila
This twin port complex, known as the Greater Alexandria Port, is supreme in terms of cargo volume, handling roughly half of Egypt’s maritime trade. Its long history, dating back to ancient times, and strategic location on the Mediterranean coast make it a natural hub for containerized cargo, general goods, and cruise ships. - Damietta
Situated at the mouth of the Nile River, Damietta specializes in containerized cargo. The port has modern facilities and closeness to major industrial zones. Its closeness to agricultural regions also makes it a key player in grain exports. - Port Said
The gateway to the Suez Canal, Port Said is used for containerized cargo and cruise ship tourism. Its strategic location makes it a vital point in global trade, connecting the Mediterranean and Red Sea. - Suez and Adabiya
This port complex on the southern end of the Suez Canal is used primarily for oil tankers and bulk cargo like coal and minerals. Its closeness to refineries and industrial zones makes it crucial for Egypt’s energy and manufacturing sectors. - Safaga
Located on the Red Sea coast, Safaga serves as a gateway for tourism and trade with East Africa.
While these key ports play a leading role, Egypt’s maritime network extends beyond them. Smaller ports like El Sokhna and Abu Qir suit specific needs, handling everything from yachts and cruise liners to oil and chemicals.
Ongoing infrastructure upgrades, automation initiatives, and free-trade zone developments aim to increase efficiency, attract new investment, and strengthen Egypt’s position as a major maritime player in the region.
How to ship heavy equipment via ocean freight?
What Are the Main Challenges When Hauling Farm Equipment to Egypt?
There are different challenges when shipping farm equipment to Egypt, let’s focus on the main ones.
Logistics
Combining ocean freight, land transport, and potentially air cargo requires navigating different regulations, paperwork, and infrastructure limitations;
Reaching rural areas with bulky machinery can be tricky due to narrow roads, weight restrictions, and insufficient storage facilities.
Bureaucracy
Clearing customs often involves delays, complex regulations, and unpredictable fees. Understanding documentation requirements and securing permits can be challenging;
Obtaining various permits and licenses for specific equipment or oversized cargo adds complexity and time to the process.
Environment and Climate
Extreme heat, dust storms, and sudden downpours can damage equipment and pose safety risks during transportation and storage;
Equipment that requires proper temperature control to prevent malfunction in Egypt’s harsh climate.
Security
Long desert routes and remote areas increase the vulnerability of equipment to damage during land transportation.
Political instability or strikes can disrupt transportation routes and pose security risks, requiring contingency plans.
What Documents Do You Need for Farm Equipment Shipping to Egypt?
Commercial Invoice
This detailed document serves as a financial contract between you and the Egyptian importer. It should include specifics like:
- Description of the equipment, including serial numbers and model numbers
- Quantity and unit price of each item
- Country of origin and manufacturer
- Total invoiced value
Bill of Lading
This shipping contract issued by the carrier acknowledges receipt of the cargo and outlines:
- Names and addresses of shipper and consignee (receiver)
- Port of origin and destination
- Description and details of the cargo
- Freight charges and payment terms
Packing List
This itemized list provides transparency and accuracy, detailing:
- Number of packages, crates, or units
- Individual packing details for each item (weight, dimensions, and so on)
- Total weight and volume of the shipment
Insurance Certificate
Protecting your investment against unforeseen damage or loss is crucial. The certificate should specify:
- Insured value of the equipment
- Covered risks (e.g., damage, theft, natural disasters)
- Policy details and contact information of the insurer
Import License (if applicable)
Certain types of equipment, like pesticides or restricted machinery, might require an import license issued by the Egyptian Ministry of Agriculture or other relevant authorities.
Additional Documents
Depending on the equipment and specific regulations, you might need:
- Phytosanitary Certificate
Verifies the plant health of agricultural equipment, often required for used machinery - Certificate of Origin
Confirms the country of origin for duty calculations - Fumigation Certificate
Required for some wooden packaging materials
What Are the Customs Regulations in Egypt?

Here’s a breakdown of what you need to know to navigate the bureaucratic jungle and ensure a smooth customs clearance for your agricultural equipment:
- Import License
Certain types of equipment require an import license - Prohibited Items
Equipment considered harmful to the environment or public health, are generally prohibited from entering Egypt - Labeling and Marking
All imported equipment must be clearly labeled in Arabic with details like country of origin, brand, model, and serial number - Inspection and Testing
Depending on the type of equipment, it might be subject to inspections and testing by the Egyptian authorities to ensure compliance with safety and technical standards
Customs Clearance
- Documentation
Prepare all necessary documents like commercial invoice, bill of lading, packing list, insurance certificate, and any relevant permits or licenses. Ensure accuracy and completeness, and consider translations into Arabic - Clearance Process
The clearance process typically involves submitting documents to the Egyptian customs authorities, paying any applicable duties and taxes, and undergoing inspections if required. Freight forwarders or customs brokers can assist with this process - Timeframe
Expect the clearance process to take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the complexity of the shipment and workload at the port
Import Duties
- Rates
The import duty for agricultural equipment in Egypt varies depending on the type and origin of the equipment. Generally, rates range from 0% to 5%, with specific exceptions for certain items - Duty Calculations
Duties are typically calculated based on the CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) value of the equipment
Taxes
- Value Added Tax (VAT)
In addition to import duties, a standard 14% VAT is applied to the total value of imported goods, including the equipment and any associated charges - Exemptions
Certain agricultural equipment used for specific purposes, like irrigation systems or crop cultivation, might be exempt from VAT
Partnering for Successful Farm Equipment Shipping to Egypt
Navigating the complexities of international shipping, customs regulations, and logistics can be a difficult thing. However, partnering with trusted partners like Atlantic Project Cargo will help you avoid this international shipping maze.
Contact Atlantic Project Cargo today for a free consultation and discover how we can simplify your farm equipment shipping to Egypt.
FAQ
Costs are constantly changing, so we recommend you Get a Quote from Atlantic Project Cargo for a piece of up-to-date information.
International rates for shipping farm equipment vary from several factors:
- Origin country
- Freight mode
- Cargo dimensions
- Customs and regulations
- Other factors
To get a detailed quote contact Atlantic Project Cargo.
The main factors that affect the price are:
- Transportation mode (ocean, air, land)
- Equipment characteristics (size, weight, value, fragility)
- Documentation and compliance (custom fees & duties, permits, licenses)
- External factors (fuel prices, exchange rates, seasonality)
The transit time depends on distance, modes of transportation, port congestion, customs clearance, seasonality, and other external factors.
Contact us today to get an estimated delivery time for farm equipment transportation.
- CPT (Carriage Paid To)
- Pros: Cost-effective for the exporter, as insurance isn’t mandatory
- Cons: Buyer assumes responsibility for customs clearance and potential risks after handover to the carrier
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To)
- Pros: Provides some security to the exporter with mandatory insurance cover
- Cons: Increases cost for the exporter compared to CPT. The buyer still handles customs clearance and post-handover risks
- FCA (Free Carrier)
- Pros: Simple for the exporter, requiring delivery to the chosen carrier but no further involvement
- Cons: Transfers significant responsibility to the buyer, including customs clearance and all transportation costs
- DAP (Delivered At Place)
- Pros: Minimizes exporter responsibility, ensuring delivery to the buyer’s specified location
- Cons: Most expensive option for the exporter, covering all transportation and customs costs
Read More



