This article explores the significant milestones in the history of tractors, describing their evolution from the first steam-powered models to the modern autonomous tractors that are revolutionizing agriculture today.
You will also learn about inventors and old tractor manufacturers who made a significant contribution to the development of tractors and the agricultural industry.
Today farming businesses contribute to economic prosperity and provide the population with food. One of the important processes in this industry is shipping agricultural equipment. Atlantic Project Cargo can become a part of your farming project and help you with tractor transportation. We offer safe and timely door-to-door delivery and cost-effective solutions.
Invention and First Development
Before the first tractor invention, farmers relied primarily on horses and bulls to do labor-intensive tasks. The appearance of steam power in the 19th century provided a more efficient and powerful alternative for agricultural work.
Steam Tractors
In 1812, Richard Trevithick built a semi-portable steam engine called the Barn Engine, which was mainly used for operating machines that separated grain from corn. He was a pioneer in developing steam-powered tractors.

In 1839, William Tuxford started the production of a truly portable engine built around a locomotive-style boiler.

Later, British engineer Thomas Aveling built the first real traction engine in 1859. He modified a Clayton & Shuttleworth portable engine and made it self-propelled. This was done by adding a long chain that linked the crankshaft to the rear axle.
The picture below is thought to be a photo of Aveling’s first traction engine. It shows the chain connecting the rear wheels to the crankshaft, with no steering mechanism in place yet.
The picture is taken from ‘Century of Traction Engines’ by W. J. Hughes. Original photo by A.R. Dibben.

This innovation transformed the agricultural industry and defined the future of tractors. From that moment farmers could cover larger areas more quickly and with less physical effort.
Gasoline Tractors
As time passed, farmers and inventors saw the need for a more practical option. The shift from steam power to internal combustion engines began in the early 1900s with the gasoline tractor invention.
John Charter built the first gasoline-powered tractor in 1889. He combined single-cylinder Otto engines with a Rumley steam engine chassis. His Charter Gas Engine Co. was the first tractor brand.

In 1892, John Froelich also built a gasoline-powered tractor. He was the first American tractor inventor, whose machine helped US farmers provide food to the population.
John Froelich attached a single-cylinder gasoline engine to the chassis and used his gearbox to control and drive it. After securing a patent, Froelich founded the Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company and invested all his resources into this venture. Unfortunately, it was unsuccessful, and by 1895, Froelich had lost everything and went out of business.

By 1903, Charles W. Hart and Charles H. Parr successfully built the first American tractor equipped with a two-cylinder gasoline engine named the “Old Number One”, Serial No. 1205. The Hart-Parr No. 1 tractor was used by its first owner for five years starting in 1901. Then it changed owners several times over the next 12 years before being disposed of shortly after World War I.
This 14,000-pound tractor only had about 30 horsepower but was more efficient and easier to operate. Today this oldest surviving internal combustion engine tractor is on display at the Smithsonian National Museum of American History in Washington, D.C.

Notably, the term “tractor” was first introduced by the Hart-Parr company.
The Golden Age
The “Golden Age” is referred to a period between the 1920s and 1940s, because some of the most iconic and influential tractors were developed during this time. Two major players in this era were Ford and John Deere.
Ford
In 1917, Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company, introduced the Fordson Model F. It was the first mass-produced tractor.

This affordable and reliable machine enabled small-scale farmers to benefit from the efficiency of tractor-powered farming, fundamentally changing the agricultural landscape.
This machine featured a 4.1-liter, four-cylinder Hercules engine producing 20 horsepower. The tractor had a three-speed transmission, including reverse, and a top speed of about 6 mph.
Its design was unique, with the engine block directly connected to the rear axle. The rear wheels came in spoked or solid steel designs, while the front wheels had a 10-spoke steel design. Later, cast iron wheels became a more affordable option.
Fordson eliminated the traditional frame, instead using the strength of the engine block to provide structural integrity.
By 1923, Fordston had 77% of the U.S. market. These tractors were produced in England, Ireland, the United States, and Russia.
John Deere
Founded in 1837, Deere & Company established itself as a trusted manufacturer of different farm equipment and made significant contributions during the Golden Age of tractors.
In the early 1900s, growing competition from the new International Harvester Company pushed John Deere to expand its product lineup. The company started making tractors, with the Dain All-Wheel-Drive being the most successful attempt. Now this oldest John Deere tractor is on permanent display at the John Deere Collectors Center in Moline, Illinois.
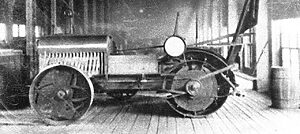
However, in 1918, Deere decided to fully enter the tractor market by buying the Waterloo Gasoline Engine Company, which produced the popular Waterloo Boy tractor in Waterloo, Iowa.
Deere continued selling tractors under the Waterloo Boy name until 1923 when it introduced the John Deere Model D. It became one of the most successful and enduring tractor models in history.

This tractor featured an improved two-cylinder engine with 27 horsepower and a top speed of 7 mph. The model remained in production for 30 years and strengthened John Deere’s reputation as a leader in farm machinery.
Other Antique Tractor Brands
Except for Ford and John Deere, other major brands produced tractors. Many early manufacturers started in similar fields, producing farming tools or other machinery. So it was a natural step for them to move into making tractors.
Oliver Corporation
The Oliver Corporation began in the mid-1800s. This was a plow-selling business started by James Oliver, which was called Oliver Chilled Plow Works.
The company was the only supplier of tractor plows for Fordson. However, as Ford began focusing more on his car business, the Oliver company realized this could threaten their business. So they started developing their tractor.
The first model, the Oliver Chilled Plow Tractor, was made in limited numbers — only about 20 were produced. These were distributed across the U.S. and received positive feedback.
The Oliver Corporation made a range of farming tools, including tractors. Then the company merged with White Motors in the mid-20th century.

J.I. Case
The J.I. Case Company was founded by Jerome Increase Case in 1842 and started as the J.I. Case Threshing Machine Co. Then the company eventually began making steam engines. They also produced machinery for the U.S. military.
In 1912, he introduced his first gasoline tractor with two cylinders, which became a good source of income.

However, the company struggled to compete with Ford’s affordable Fordson and was sold to Massey-Harris in 1928.
Massey-Ferguson
Massey-Ferguson originally began as Massey-Harris. It started making tractors during World War I due to high food demand.
Unlike many other firms during the Great Depression, Massey-Harris thrived while Ford’s sales dropped. It succeeded especially after acquiring the J.I. Case Plow Works, making them a top tractor manufacturer.
The company produced its first tractor ‘the General Purpose’ in 1930.
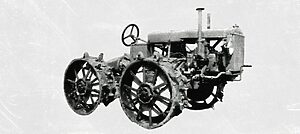
Massey-Harris changed its name to Massey-Ferguson in 1953 after buying the Ferguson-Brown company.
Allis-Chalmers
Edward Allis founded the Allis-Chalmers company in 1861. He bought a business that produced sawmills and flour mills during an economic downturn. The company survived the financial crisis of 1873 and was renamed Edward P. Allis & Company under his leadership.
By the time he died in 1889, Allis had turned his company into a leading manufacturer of sawmills and flour mills, as well as a major producer of steam engines. So, it made sense for the newly named Allis-Chalmers to start making tractors using their steam engines.

In 1931, this orange tractor brand bought the struggling Advance-Rumely Thresher Company, which helped them become one of the most successful tractor manufacturers right after International Harvester and John Deere.
International Harvester
International Harvester was formed by combining five different companies. Two of these, McCormick and Deering, had been rivals for years and struggled to agree on a merger. In 1902, negotiations did take place, leading to the creation of one of the most famous tractor companies in history, International Harvester.
The company was known for its innovations, including the first commercial power take-off tractor in 1919 and the first row-crop tractor, the Farmall. The Farmall brand was so successful that by the 1930s, International Harvester held 44% of the American market.

If you have a business, our company can contribute to its development. We can assist with heavy machinery shipping, e.g. tractors, combine harvesters, seeders, and more. We offer top-quality domestic and international transportation services, as well as insurance, customs brokerage, and fumigation.
Technological Modernization
As many manufacturers entered the market, competition increased, leading to a wider range of tractor options and lower prices. These developments made tractors more accessible and revolutionized farming worldwide.
In the mid-20th century, tractors experienced key improvements that made them even more efficient and versatile.
One major change was the switch to diesel-powered engines. These engines had several benefits over gasoline ones, such as using less fuel, providing more power, and lasting longer.
Another important improvement was the addition of hydraulic systems and power take-offs (PTOs).
Hydraulic systems allowed tractors to use fluid power to run different attachments, making it possible for them to do much more than just plowing or tilling.
PTOs were also a game-changer — they let tractors directly power attached equipment. Mowers, balers, plows, or Gannon graders were all powered off the tractor. This made tractors essential on modern farms since one machine could handle many different jobs efficiently.

The Growth of Smart Farming
In recent years, farming has embraced a digital revolution with technologies like GPS, data analysis, advanced sensors, and Artificial Intelligence. These significant advancements are paving the way for precision farming.
GPS and Analytics
Modern tractors navigate fields with accuracy, using GPS and real-time data. These technologies improve planting, fertilizing, and watering. They ensure seeds are planted at the right depth and spacing, and fertilizers or pesticides are applied precisely where needed.
This approach boosts crop yields, saves resources, and supports sustainable farming practices.
Smart Cab
Modern farmers are looking for tractor models equipped with touchscreen controls, climate-controlled interiors, camera displays, and lights that respond to eye-motion sensors.
These tractors may also offer manual and automated operation modes. This makes farming tasks easier in different weather conditions, enabling longer working hours. Such advancements enhance the farming experience and help increase farm productivity.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technology allows farmers to control their machines remotely using mobile phones or computers. Many tractor brands already offer this connectivity.
In the future, farmers may not even need to enter the field to manage their operations. This innovation streamlines farming tasks and brings new levels of efficiency to agriculture.
High Horsepower Tractors
Tractor manufacturers have developed models with high engine power and horsepower to make farming tasks more efficient. Some of these models may exceed 800 hp. For example, the John Deere 9RX 830 Tractor has a 6-cylinder engine with 830 hp rated power and 913 hp maximum power.
These advancements allow tractors to handle heavy-duty operations and cover larger areas in less time.
Data-Collecting Tractors
These tractors are equipped with sensors that gather data on essential farming factors, like soil moisture levels or weather conditions.
Access to this information helps farmers make better decisions, leading to higher production. Such technology ensures that every aspect of farming is optimized for better yields and profitability.
Autonomous Electric Tractors
Another major innovation is the rise of self-driving tractors. These machines perform tasks without human control. They use a multi-camera system, LiDAR, and radar sensors to detect objects, humans, and animals, which improves safety during operations.
Another advantage of autonomous tractors is that they can navigate fields without crop damage and facilitate longer work hours.

Although still in early use, they promise to lower labor costs and reduce the chance of accidents.
Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
Robotics and AI are revolutionizing agriculture, bringing greater efficiency and precision. The examples include robotic arms that can carefully pick fruit, and AI-powered tractors that identify and target weeds, reducing herbicide use.
Sensors and cameras with AI analytics enable data-driven decisions, allowing tractors to manage crops in real-time without human input.
Conclusion
The history of tractors highlights human creativity and the constant desire to improve farming methods, harvest quality, and reduce human labor. From early steam-powered machines to today’s advanced technology, each stage has brought new ideas that have changed the agricultural sector.
If you have a tractor, used or modern, or even antique, and need to transport it, contact Atlantic Project Cargo. We offer top-quality shipping services and ensure your farm equipment will reach its destination quickly and safely.
If you’re looking to purchase a tractor, many buyers choose to buy tractors on JumboBee and then move on to arranging transport and delivery.
Read More


