Celebrated every May, World Trade Month is a time to recognize the importance of international trade. It highlights how trade between countries creates jobs, opens new business opportunities, and strengthens the global economy as a whole. The United States has been celebrating it since 1938, and many events and programs are held throughout the month to promote its significance.
World Trade Month wouldn’t be complete without acknowledging the agricultural sector’s critical role. Here’s how agriculture contributes significantly to global commerce:
- Food Security: International trade allows countries to import the food they don’t produce enough of, ensuring a wider variety and stable supply for consumers around the world.
US agricultural imports
- Economic Growth: Agricultural exports are a major source of income for many countries, boosting their economies and contributing to global trade value.
- Efficiency and Innovation: Trade fosters competition, encouraging innovation and efficiency in agricultural practices to stay competitive in the global market.
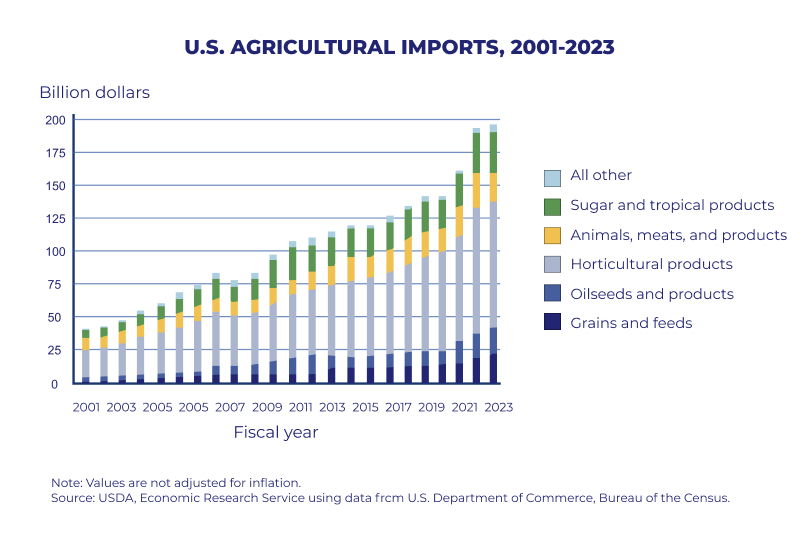
While vital, agricultural trade faces hurdles. Regulations and tariffs can make it expensive and complex to export agricultural products. Countries around the world tend to impose higher tariffs on agricultural products compared to non-agricultural goods. In fact, studies show this happens in over 90 percent of countries.
Events like political instability or climate change can disrupt supply chains and cause price fluctuations. Here we can mention conflict in Ukraine, the Red Sea crisis, or El Nino and La Nina weather patterns.
But there are opportunities too. A rising global population creates a constant demand for food imports, opening markets for efficient producers. According to projections, feeding a global population of 9.1 billion in 2050 would necessitate a 70 percent increase in overall food production (FAO: Global Agriculture Towards 2050).
Trends, Growth Areas, and Challenges for Agricultural Trade
Recent trends in agricultural trade paint a complex picture, with both growth and challenges.
Growth Trends
Despite a projected slowdown, global agricultural trade continues to expand, with a significant rise in volume and value compared to overall world trade. The total value of agricultural production worldwide is expected to reach US$3.9 trillion in 2024. This number is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 5.66% over the next four years, reaching US$4.86 trillion by 2028 according to Statista.
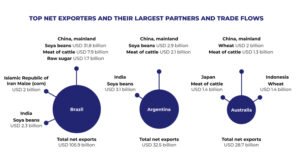
Traditionally dominant players like the US and EU are seeing competition from emerging markets like China, Brazil, Argentina, and Australia, who are ramping up production and exports.
Trade is becoming more “globalized,” with countries expanding their trade partnerships beyond traditional allies.
Emerging Markets and Growth Areas
Demand is rising for products like fruits, vegetables, and meat, particularly in developing countries with growing middle classes. Demand for agricultural products in developing countries is expected to grow faster than their production capacity. Consequently, these countries are projected to account for 92% of the global increase in meat imports, 92% of the increase in grain and oilseed imports, and nearly all of the rise in world cotton imports (Developing Countries Dominate World Demand for Agricultural Products, Ronald Trostle and Ralph Seeley).
Consumers are increasingly interested in ethically and sustainably produced food, creating a potential export niche for countries with strong sustainability practices. A recent survey by Cargill, a major agricultural services and food production company, shows that consumers are paying more attention to sustainability when buying food. The company’s FATitudes Survey polled 6,000 shoppers in 11 countries and found that more than half (55%) are now more likely to buy a product with a sustainability claim, compared to 51% in 2019.
Trade in crops used for biofuel production is on the rise, driven by the push for renewable energy sources. Five countries contribute 80% of the growth in global biofuel consumption. For biodiesel, these are the United States, Indonesia, and Brazil. For ethanol, they are Brazil, India, and Canada (OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2023-2032).
Challenges
Geopolitical disputes can lead to trade wars and tariffs, disrupting established trade flows and raising food prices. Caldara and Iacoviello in their work “Measuring geopolitical risk” identify several ways geopolitical risks disrupt agricultural exports. These risks can lead to:
- Higher export costs. The cost of shipping agricultural goods can increase due to factors like disruptions in transportation routes or higher fuel prices
- Increased security spending. Exporters may need to invest more in security measures to protect their products during transport, especially in high-risk regions
- Reduced insurance coverage. Insurance companies may be less willing to cover shipments in areas with heightened geopolitical tensions, making it more expensive or even impossible for exporters to obtain adequate coverage
Extreme weather events and resource scarcity can disrupt agricultural production and impact food security, making trade even more crucial (The impact of extreme climate events on agricultural production in the EU, Study Requested by the AGRI Committee).
Overall, the future of agricultural trade is dynamic. New players are emerging, consumer preferences are evolving, and technological advancements can reshape the landscape. The ability to navigate these challenges and capitalize on growth areas will be key for countries to succeed in the global agricultural market.
Opportunities for Agricultural Trade
The current economic climate presents both challenges and opportunities for agricultural trade. Here are some specific areas with strong potential.
Technological Advancements in Agriculture
The global agricultural sector is experiencing a surge in demand for advanced equipment. This trend is driven by several factors:
- Feeding a world population projected to reach 9.1 billion by 2050 necessitates significant increases in food production
- As incomes rise in developing countries, the demand for meat, dairy, and processed foods increases, putting pressure on agricultural output
- The agricultural industry faces a shrinking workforce in many regions. Precision agriculture equipment helps address this by automating tasks and improving efficiency
- Farmers are increasingly adopting practices that minimize environmental impact. Precision agriculture technologies like variable-rate application and data-driven resource management contribute to sustainable farming
This rising demand translates into a need for efficient and reliable transportation of agricultural equipment. Atlantic Project Cargo specializes in handling large and complex agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, planters, and sophisticated harvester attachments. Additionally, Atlantic Project Cargo’s global network allows them to facilitate the transport of this equipment from manufacturers to farms around the world.
New Trade Agreements
Countries are increasingly looking to regional trade agreements to reduce barriers and create new opportunities for trade with neighboring countries. This can create more stable and predictable markets for agricultural products. A study analyzing tariff concessions in various trade agreements (RTAs) found that preferential margins, the advantage given to member countries by lower tariffs, increase significantly over time. On average, these margins rise from 4.7% to 8.9% about eight years after the agreements take effect. (“Regional trade agreements and agriculture”, OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Papers, No. 79, OECD Publishing, Paris).
Niche Markets
As we mentioned earlier, consumers are increasingly interested in food that is produced organically and with sustainable practices. Countries with strong organic farming sectors can cater to this growing demand and potentially command premium prices for their products.
Foods with added health benefits are gaining popularity. Countries that can develop and export these types of products can carve out a niche in the global market.
Innovation in Food Processing and Transportation
Advancements in storage and transportation technologies can help reduce food spoilage and waste, allowing for more efficient trade of perishable agricultural products. This can open up new markets for countries that previously couldn’t export certain types of food due to logistical limitations.
How Shipping and Logistics Drive American Prosperity
USCG MARITIME COMMERCE STRATEGIC OUTLOOK
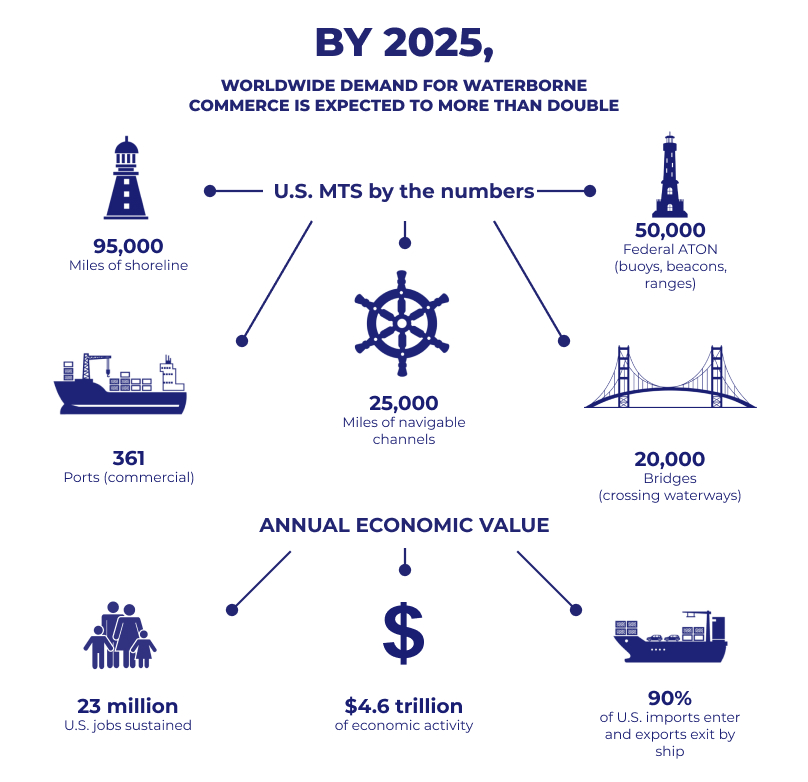
The United States prospers from global trade, and behind every imported good and exported product lies a complex web of shipping and logistics. These services ensure the smooth flow of goods across vast distances, playing a vital role in the US economy, especially for the agricultural sector.
Massive container ships carry the bulk of US imports and exports. Logistics companies manage the entire supply chain, from warehousing and inventory management to customs clearance and documentation. They ensure goods reach their destination efficiently and cost-effectively. A strong regulatory framework ensures safety and security in shipping. Additionally, well-maintained ports, rail networks, and highways keep goods moving efficiently.
Why Shipping and Logistics Matter for US Agriculture
The agricultural sector is a major contributor to the US economy, and efficient shipping and logistics are crucial for its success:
- Reaching Global Markets
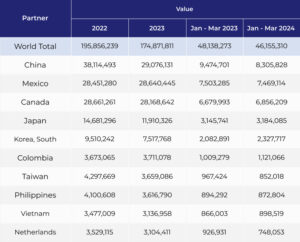
US farmers can export their products to a wider audience, increasing their income and fostering economic growth. Countries like China and Japan rely heavily on US agricultural imports. According to data from fiscal year 2023, the top five export destinations for US agricultural products accounted for a substantial 64% of the total value of US agricultural exports. China ranked as the leading importer, with a value of $33.7 billion in US agricultural goods. Mexico and Canada followed closely behind, importing $28.2 billion and $27.9 billion worth of US agricultural products, respectively. (Economic Research Service, U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE) - Competitive Advantage
Efficient logistics reduce costs and delivery times, giving US agricultural products a competitive edge in the global market. Fresh produce can reach distant markets while still maintaining quality - Ensuring Food Security
The US imports certain food products it doesn’t produce enough of. Efficient logistics ensure a wider variety and stable supply of food for American consumers
The US continues to invest in modernizing its shipping infrastructure and streamlining logistics processes. By embracing innovation and addressing challenges, the US can ensure that shipping and logistics remain the lifeblood of US trade and continue to drive prosperity, especially for the agricultural sector.
Additionally, companies specializing in oversized cargo like Atlantic Project Cargo play a vital role by handling the transportation of complex agricultural machinery, ensuring farms around the world have the equipment needed to thrive.
Resources and Support Available for Businesses Looking to Expand Their Agricultural Trade Activities
- Government Agencies
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS)
The FAS provides a wealth of information and support for US agricultural exporters. They offer market research reports, trade missions, technical assistance, and programs to help businesses comply with export regulations. Similar agencies exist in most countries around the globe - Ministry of Trade or Commerce
Many governments have dedicated ministries or departments that focus on promoting international trade. These agencies often offer export financing programs, trade promotion events, and guidance on navigating trade regulations
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS)
- Trade Associations
- Industry-Specific Associations
Numerous industry associations cater to specific agricultural sectors, such as the National Cattlemen’s Beef Association or the American Fruit Growers. These associations can provide valuable insights, networking opportunities, and resources specific to your agricultural product - General Trade Associations
Organizations like the International Trade Administration (ITA) or the National Foreign Trade Council (NFTC) offer a wider range of resources and support for businesses of all sizes engaged in international trade
- Industry-Specific Associations
- International Trade Financing Options
- Export Credit Agencies (ECAs)
These government-backed institutions offer loans, guarantees, and insurance to help businesses finance their exports. ECAs can mitigate risks associated with international trade, such as non-payment by foreign buyers. Search for your country’s specific ECA - Private Banks
Many commercial banks have specialized international trade finance departments that offer a variety of financing options for exporters. These options may include letters of credit, working capital loans, and export factoring
- Export Credit Agencies (ECAs)
- Additional Resources
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
The WTO provides a wealth of information on international trade rules and regulations. Their website offers resources on everything from tariffs to sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
Conclusion
World Trade Month serves as a timely reminder of the critical role agriculture plays in international commerce. From ensuring global food security to fostering economic growth, agricultural trade is a complex and dynamic system. While challenges like trade barriers and climate change persist, exciting opportunities are emerging. Technological advancements, a growing demand for sustainable practices, and the rise of niche markets all point toward a future filled with potential. Businesses that embrace innovation, navigate challenges strategically and leverage available resources are well-positioned to thrive in this ever-evolving global landscape. As the world’s population continues to grow and consumer preferences shift, agricultural trade will remain a cornerstone of global economic prosperity and a driver of progress for nations around the world.
Companies like Atlantic Project Cargo play a crucial role in this ecosystem by facilitating the movement of oversized and specialized agricultural equipment. Their expertise in customized solutions, navigating regulations, and utilizing alternative transport methods ensures this vital equipment reaches farms around the world. By capitalizing on emerging trends like the demand for sustainable practices and technological advancements, agricultural businesses can thrive in the global market. With the support of available resources and a commitment to efficient logistics, the future of agricultural trade remains bright.
Read More


